Spectra of electrons
reflected from the
![]() homogeneous
targets
homogeneous
targets
![]() Nb/Si two-layer
targets
Nb/Si two-layer
targets
![]() Nb/Al/Nb/Si multilayer
targets
Nb/Al/Nb/Si multilayer
targets
![]() nitrogen
implanted Nb target
nitrogen
implanted Nb target
Experimental
setup
![]() Vacuum
chamber
Vacuum
chamber
![]() Electron beam
Electron beam
![]() Energy
analyzer
Energy
analyzer
![]() Targets
Targets
Experimental setup
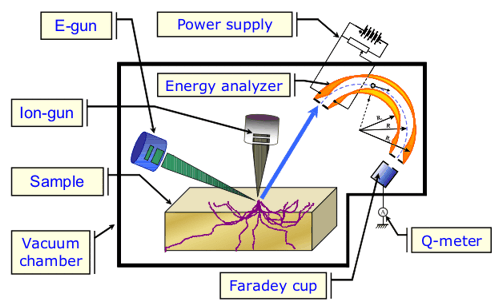
The stainless steel vacuum chamber withstands
bake-out up to 300°C. The vacuum system is oil-free: preliminary
pumping- by turbo-molecular pump; finally during experiment - by means
of two magneto-discharge pumps (with the turbo-molecular pump cut off).
Residual pressure during the experiment is kept below 10-6 Pa
with no hydrocarbons found with mass spectrometry.
The specimen surface is cleaned by in situ Ar-ion sputtering at 5 keV
ion energy and current density of 1.5 mA/cm2. If necessary,
the target can be heated by a defocused electron beam of current 300 mA
and accelerating voltage 20 kV up to 500° C. The purity of the target
surface is proved by observing the peak of elastically reflected
electrons. Neither electron-assisted growth of hydrocarbon films, nor
other changes of the subsurface structure of the target due to Ar-ion
bombardment takes place in the experimental setup.
The probing electron beam of energy E0 is variable between 3 and 30 keV. The electron beam current is kept at a level of 125 mkA. Virtually no heating of target appears. The experiment geometry is such that the energy analyzer receives electrons reflected from the target surface at the angle J= 135° (that is 45° to the target’s normal).
The energies of reflected electrons are detected by a 180° spherical electrostatic energy analyzer with a resolution DE/E0 = 0.8%. The voltage applied to the analyzer plates varies between 0 to 4 kV. The electrons passed through the analyzer proceed into a Faraday cup. The Faraday cup current (10-12 to 10-10A) is registered by an electrometric amplifier with an absolute resolution of 10-13A.
Nb/Si and Nb/Al/Nb/Si targets have been prepared
on a Si(100) phosphorus-doped, 4.5 Ohm cm substrates using Leybold
L560 magnetron sputtering system (Moscow State University), at a
base pressure level of 2 10-5Pa. Before deposition
substrates were sputter cleaned in glow discharge of Ar at a
pressure of 0.5Pa for 150s. Subsequently, the sputtering of Nb and
Al has been carried out at Ar pressure of 1 Pa. The thicknesses of
the Nb and Al layers have been measured with a Taylor–Hobsen
profilometer and, independently, using the Michelson interferometry
method. Multiple measurements showed an error within 10%. The rates
of Nb and Al evaporation were found to be 2.34 and 0.16 nm/s,
respectively.
Nb/Si, Nb/Al/Si, Nb/AlOx-Al/Si and Nb/Al-AlOx/Nb/Si have
been prepared on a Si(100) phosphorus-doped, 10 Ohm cm substrates
using Pfeiffer SLS-630G magnetron sputtering cluster tool (Chalmers
University of Technology), at a base pressure level of 2 10-6Pa.
Before deposition substrates were sputter cleaned in glow discharge
of Ar at a pressure of 1Pa for 60s. Subsequently, the sputtering of
Nb and Al has been carried out at Ar pressure of about 1Pa,
oxidation of Al layer has been carried out in a flow of a of pure
dry oxygen at a pressure of about 10Pa in the load-lock. The
thicknesses of the Nb and Al layers have been measured with a Tencor
P-2 profilometer. Multiple measurements showed an error
within 2%. The rates of Nb and Al evaporation were found to be 0.95
and 0.3 nm/s, respectively.